Topics
The set of topics comprises an integrated and coherent presentation that starts with ill-posedness and regularization, develops mathematical and computational tools for sensitivity analysis and deterministic inversion for problems governed by differential equations via nonlinear least squares optimization, and elaborates a framework for formulation and solution of Bayesian inverse problems, building on several of the deterministic tools.
Morning lectures will be followed by hands-on afternoon lab sessions, where students will employ the methods presented in the lectures using state-of-the-art software and explore issues more deeply.
The summer school will culminate with presentations of projects the students have worked on in small teams during the latter part of the second week.
Morning lectures
- Introduction to inverse problems, ill-posedness, regularization
- Numerical optimization methods
- Variational calculus, first and second-order sensitivity
- Adjoint methods and PDE-constrained optimization
- Bayesian statistical framework
- Linear-Gaussian Bayesian inverse problems
- MCMC for general nonlinear Bayesian inverse problems
- Advanced topics in Bayesian computation I: Infinite-dimensional Bayesian inversion
- Advanced topics in Bayesian computation II: Sequential inference, optimal experimental design
Afternoon hands-on lab sessions
- Getting started with Python (installation, Docker)
- Introduction to FEniCS (weak forms, solving PDEs via FEniCS)
- Variational calculus problems via hiPPYlib
- Solving inverse problems via hIPPYlib
- Simple examples in Bayesian computation and Monte Carlo methods
- Linear Bayesian inversion via MUQ–hIPPYlib
- MCMC methods via MUQ–hIPPYlib
- Project work
- Project work
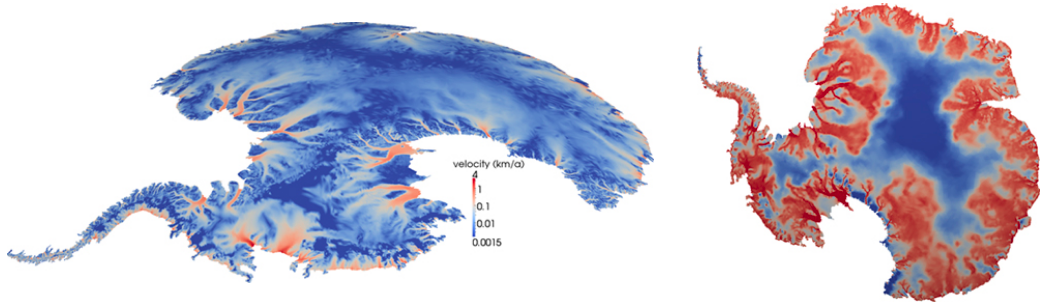
Left: Satellite observations of surface ice flow velocity used to solve Antarctic ice sheet inverse problem, along with a model of ice flow as a non-Newtonian fluid. Right: Inferred basal friction parameter field (warm colors imply low resistance to sliding at base of ice sheet)