Demonstration of Gaussian Processes
import sys
sys.path.insert(0,'/home/fenics/Installations/MUQ_INSTALL/lib')
import pymuqModeling as mm
import pymuqApproximation as ma
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
One Spatial Dimension
xDim = 1
yDim = 1
numPts = 300
x = np.zeros((1,numPts))
x[0,:] = np.linspace(0,1,numPts)
mean = ma.ZeroMean(xDim,yDim)
# How many samples to plot for each kernel
numSamps = 3
def PlotSamples(gp):
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
for i in range(numSamps):
plt.plot(x[0,:], gp.Sample(x)[0,:])
plt.xlabel('Position $x$', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel('Field Value $y$', fontsize=16)
plt.show()
def PlotKernel(kern):
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
numPlot = 100
xs = np.zeros((1,numPlot))
xs[0,:] = np.linspace(0,1,numPlot)
base = np.array([0])
ks = np.zeros((numPlot))
for i in range(numPlot):
ks[i] = kern.Evaluate(base,xs[:,i])[0,0]
plt.plot(xs[0,:], ks,linewidth=3)
plt.xlabel('Distance, $\|x-x^\prime\|$', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel('$k(x,x^\prime)$', fontsize=16)
plt.ylim([0,1.1*np.max(ks)])
plt.show()
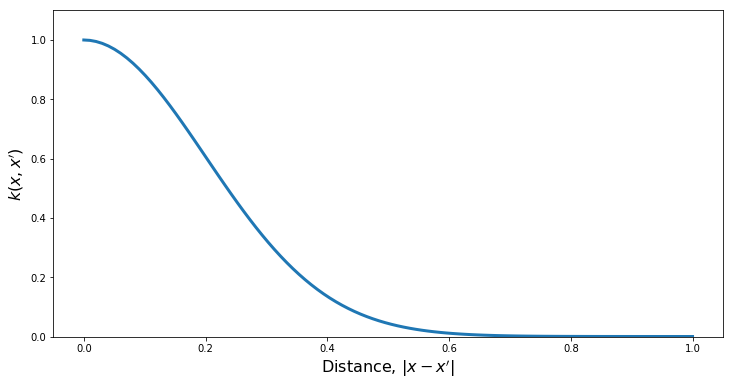
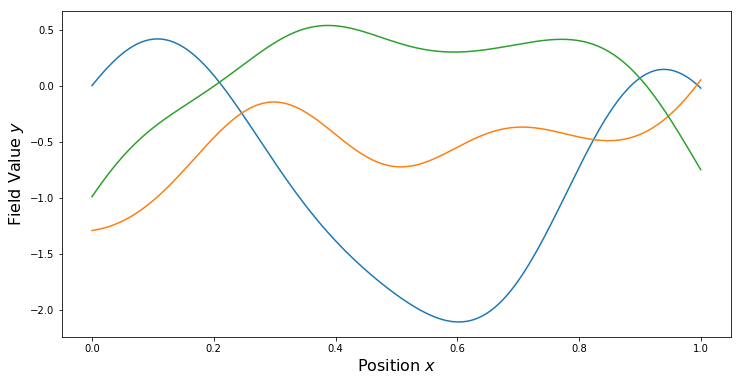
Squared Exponential Kernel
var = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
length = 0.2 # Lengthscale of the kernel
kern = ma.SquaredExpKernel(xDim, var, length)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)
PlotSamples(gp)
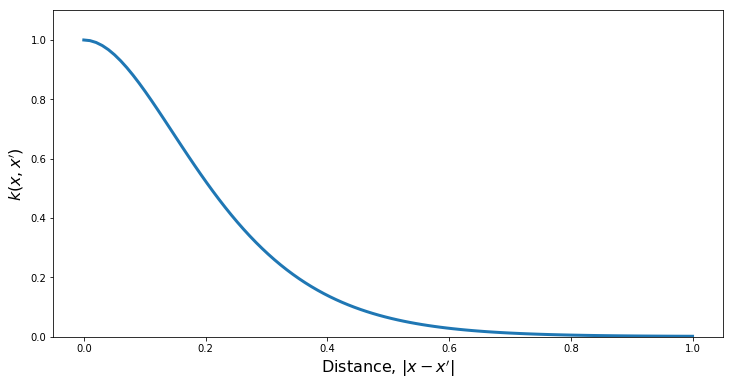
Matern Kernel
var = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
length = 0.2 # Lengthscale of the kernel
nu = 5.0/2.0 # Smoothness parameter
kern = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, var, length, nu)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)
PlotSamples(gp)
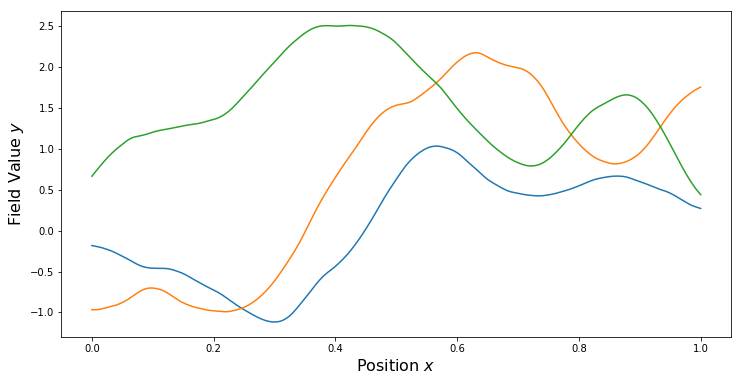
nu = 3.0/2.0 # Smoothness parameter
kern = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, var, length, nu)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)
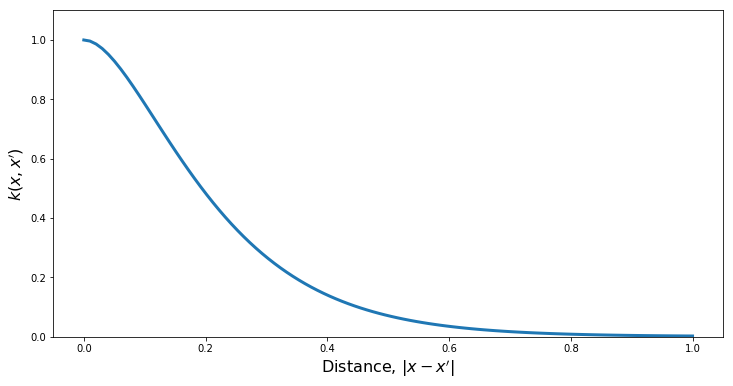
PlotSamples(gp)
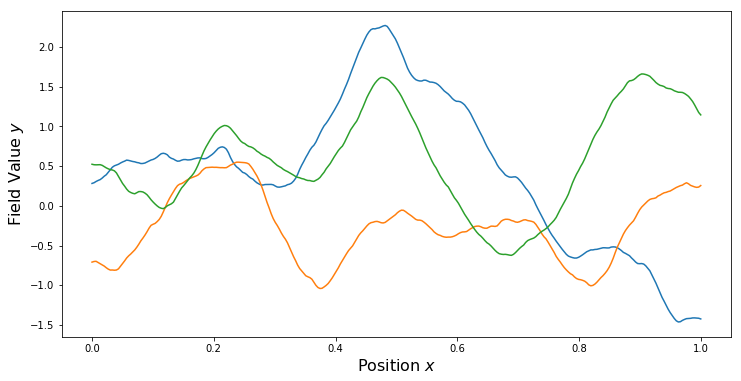
nu = 1.0/2.0 # Smoothness parameter
kern = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, var, length, nu)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)
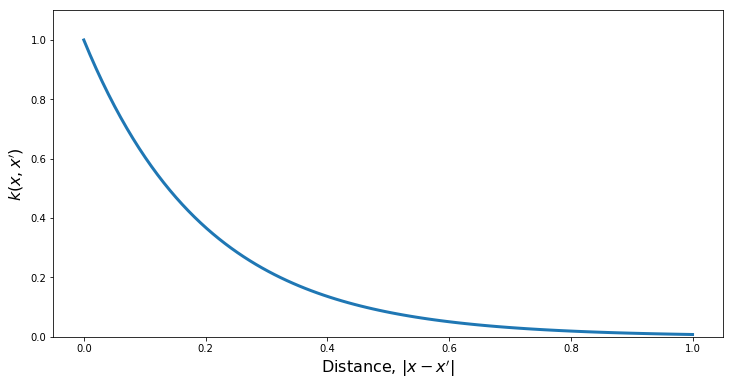
PlotSamples(gp)
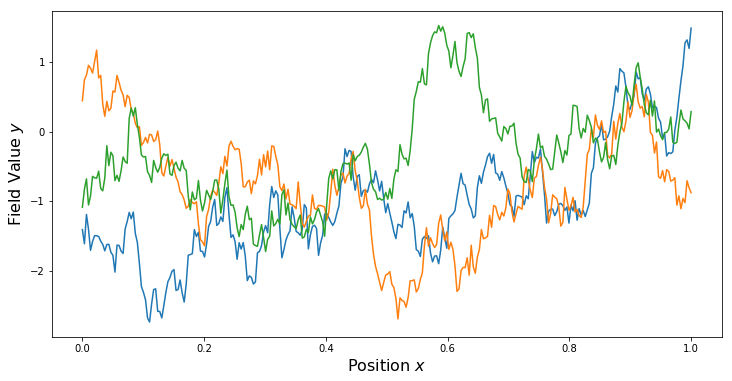
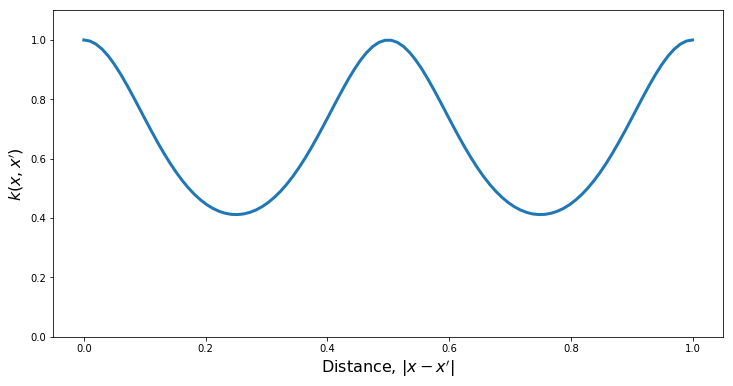
Periodic Kernel
var = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
length = 1.5 # Lengthscale of the kernel
period = 0.5 # Period
kern = ma.PeriodicKernel(xDim, var, length, period)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)
PlotSamples(gp)
Constant Kernel
var = 1.0
kern = ma.ConstantKernel(xDim, var)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)

PlotSamples(gp)

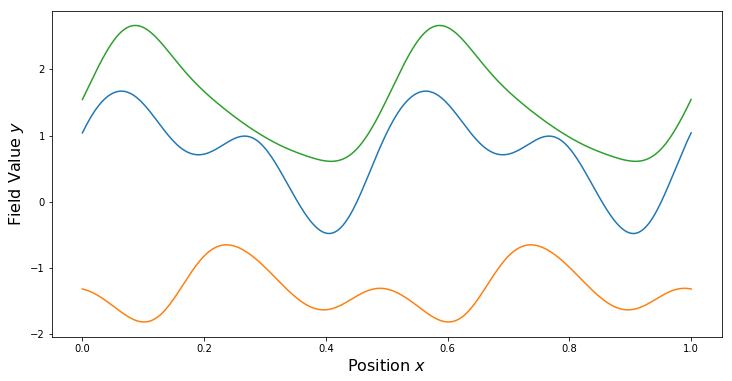
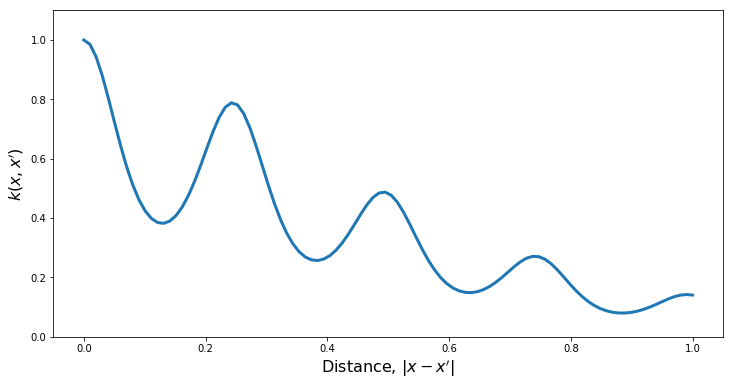
Quasi-Periodic Kernels
For some non-periodic kernel $k_2$ and a periodic kernel $k_{per}$, a quasi-periodic kernel can be formed through the product.
perVar = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
perLength = 1.5 # Lengthscale of the kernel
perPeriod = 0.25 # Period
matVar = 1.0 # Matern Variance
matLength = 0.5 # Matern Length
matNu = 3.0/2.0 # Matern Smoothness
kern1 = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, matVar, matLength, matNu)
kern2 = ma.PeriodicKernel(xDim, perVar, perLength, perPeriod)
kern = kern1*kern2
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)
PlotSamples(gp)
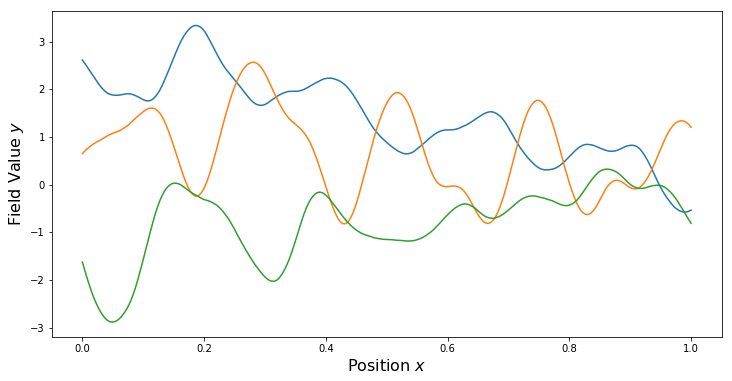
Sum Kernels
constVar = 50.0
matVar = 1.0
matLength = 0.2
matNu = 1.0/2.0
kern1 = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, matVar, matLength, matNu)
kern2 = ma.ConstantKernel(xDim, constVar)
kern = kern1 + kern2
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotKernel(kern)

PlotSamples(gp)
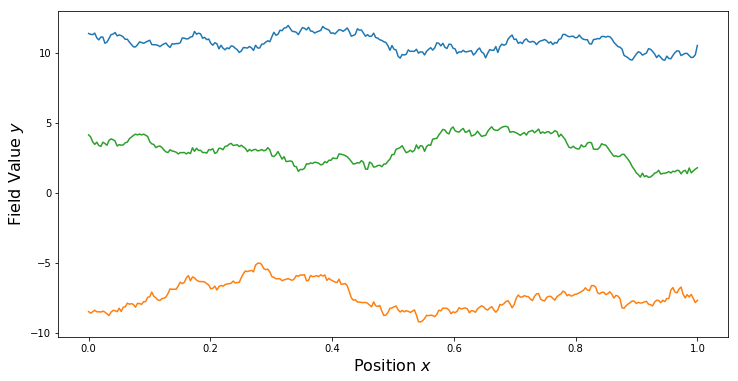
Two Spatial Dimensions
numPts = 40
xDim = 2
yDim = 1
# Construct the grid points
x1 = np.linspace(0,1,numPts)
x2 = np.linspace(0,1,numPts)
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(x1,x2)
x = np.zeros((2,numPts*numPts))
x[0,:] = X1.ravel()
x[1,:] = X2.ravel()
mean = ma.ZeroMean(xDim,yDim)
numSamps = 3
def PlotSamples2d(gp):
gauss = gp.Discretize(x)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=numSamps, figsize=(16,5))
for i in range(numSamps):
samp = gauss.Sample()
axs[i].pcolor(X1, X2, np.reshape(samp, (numPts,numPts)))
axs[i].set_title('Sample %d'%i)
plt.show()
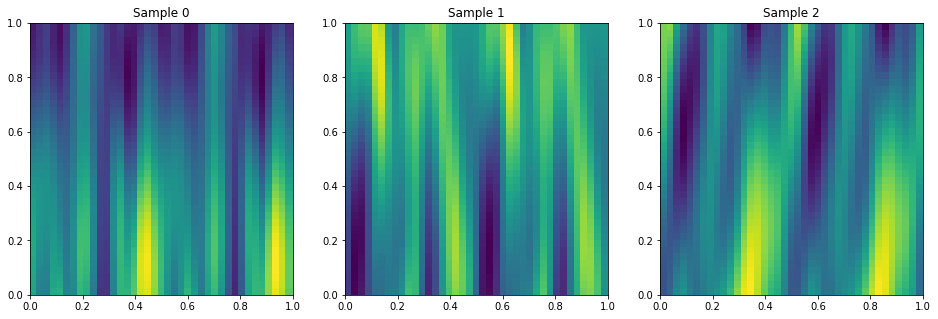
Isotropic Matern
var = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
length = 0.2 # Lengthscale of the kernel
nu = 5.0/2.0 # Smoothness parameter
kern = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, var, length, nu)
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotSamples2d(gp)
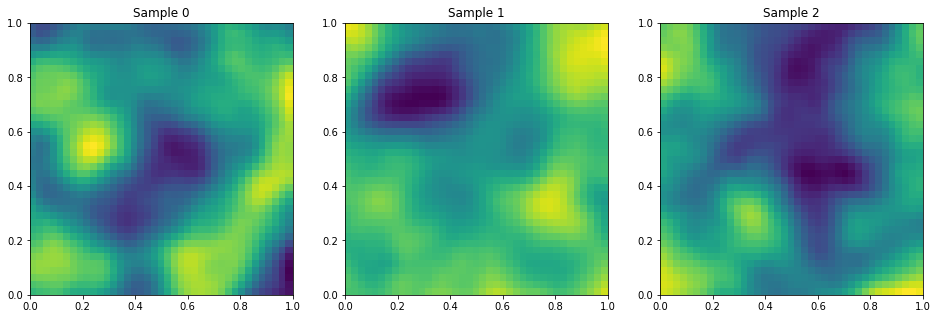
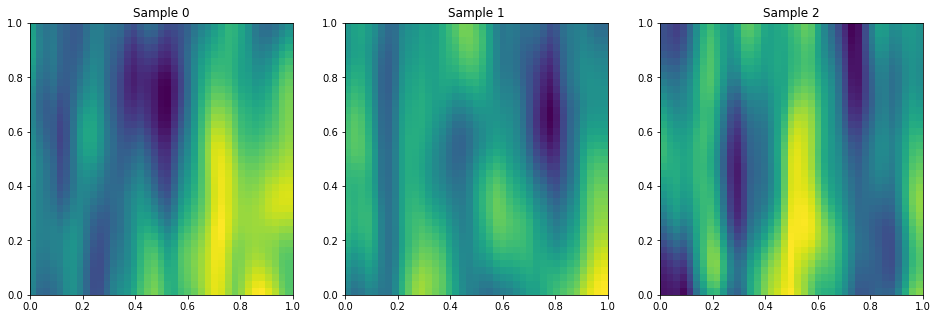
Anisotropic Matern
var = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
length1= 0.1 # Lengthscale of the kernel in the x_1 direction
length2= 0.4 # Lengthscale of the kernel in the x_1 direction
nu1 = 5.0/2.0 # Smoothness in x1
nu2 = 5.0/2.0 # Smoothness in x2
kern1 = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, [0], var, length1, nu1)
kern2 = ma.MaternKernel(xDim, [1], var, length2, nu2)
kern = kern1*kern2
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotSamples2d(gp)
Periodic in X1, Squared Exp. in X2
var = 1.0 # Marginal Variance
length1= 0.5 # Lengthscale of the kernel in the x_1 direction
length2= 0.4 # Lengthscale of the kernel in the x_1 direction
period1 = 0.5
kern1 = ma.PeriodicKernel(xDim, [0], var, length1, period1)
kern2 = ma.SquaredExpKernel(xDim, [1], var, length2)
kern = kern1*kern2
gp = ma.GaussianProcess(mean, kern)
PlotSamples2d(gp)